Biotechnology in Remediation: Innovations for Environmental Clean-up
Introduction
Environmental contamination is a significant challenge facing industries and governments worldwide. Traditional methods of cleanup are often costly, time-consuming, and not entirely effective. Biotechnology offers innovative solutions for environmental remediation, harnessing the power of living organisms to clean up pollutants in a more sustainable and efficient manner. This blog delves into the latest biotechnological advancements in environmental cleanup and their potential impact on the future of remediation efforts.
Table of Contents
1. Understanding Bioremediation
2. Key Biotechnological Innovations in Remediation
3. Case Studies: Successful Bioremediation Projects
4. Challenges and Considerations
5. Future Prospects for Biotechnological Remediation
6. Conclusion
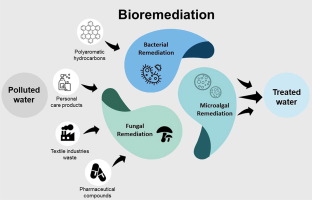
Understanding Bioremediation
Bioremediation is a process that uses microorganisms, plants, or enzymes to detoxify and remove pollutants from the environment. This approach leverages the natural abilities of these organisms to degrade harmful substances into less toxic forms, making it a sustainable alternative to chemical and physical remediation methods.
Key Biotechnological Innovations in Remediation
Recent advancements in biotechnology have led to the development of more effective and targeted remediation techniques. These include:
- Genetically Engineered Microorganisms (GEMs): Scientists have created GEMs capable of breaking down specific pollutants that natural organisms cannot.
- Phytoremediation: The use of plants, such as willows and poplars, to absorb and degrade contaminants from soil and water.
- Enzyme-Based Remediation: Enzymes derived from microorganisms or plants are used to catalyze the breakdown of pollutants.
Image: Phytoremediation in action, using plants to clean up contaminated soil.
Case Studies: Successful Bioremediation Projects
- Oil Spill Cleanup: GEMs were successfully deployed to degrade oil spills in marine environments, significantly reducing the ecological impact.
- Heavy Metal Removal: Phytoremediation has been used to remove heavy metals like lead and arsenic from contaminated soils in industrial regions.
- Pesticide Degradation: Specific microorganisms have been engineered to break down persistent pesticides, preventing them from entering the food chain.
"Biotechnology offers a promising path forward in environmental remediation, combining efficiency with sustainability." — Environmental Scientist
Challenges and Considerations
While biotechnology offers exciting possibilities, there are challenges to consider. These include the regulatory hurdles associated with the release of genetically modified organisms (GMOs), the potential for unintended ecological impacts, and the need for extensive research to ensure the safety and effectiveness of these technologies.
Future Prospects for Biotechnological Remediation
The future of biotechnological remediation looks promising, with ongoing research aimed at enhancing the capabilities of microorganisms and plants to tackle more complex pollutants. Innovations such as synthetic biology, which involves designing organisms from scratch, could revolutionize the field by creating tailor-made solutions for specific environmental challenges.
Conclusion
Biotechnology is paving the way for more efficient and sustainable methods of environmental cleanup. As research continues to advance, bioremediation could become the preferred approach for tackling a wide range of environmental contaminants, offering hope for a cleaner, healthier planet.